Dynamic vs. Static Data Structures, Pointers, and Structures
-
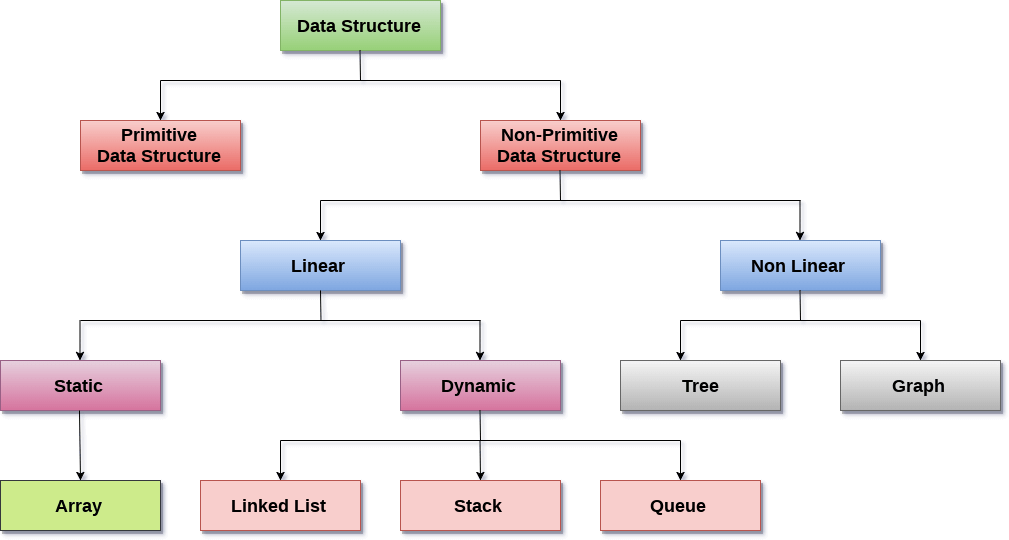
Introduction
-
Static Data Structures
-
Dynamic Data Structures
-
Difference Between Static and Dynamic Data Structures
-
Pointers
-
Role of Pointers in Dynamic Data Structures
-
Structures in C++
-
Structures with Pointers
-
Real-World Use Cases
-
Conclusion
Visit previous lesson: ArrayList and Operations
1. Introduction
Efficient data handling is a core requirement of modern software systems. Depending on application needs, data may be fixed in size or may change dynamically at runtime.
This leads to the concepts of static data structures, dynamic data structures, pointers, and structures, all of which are fundamental in C++ programming.
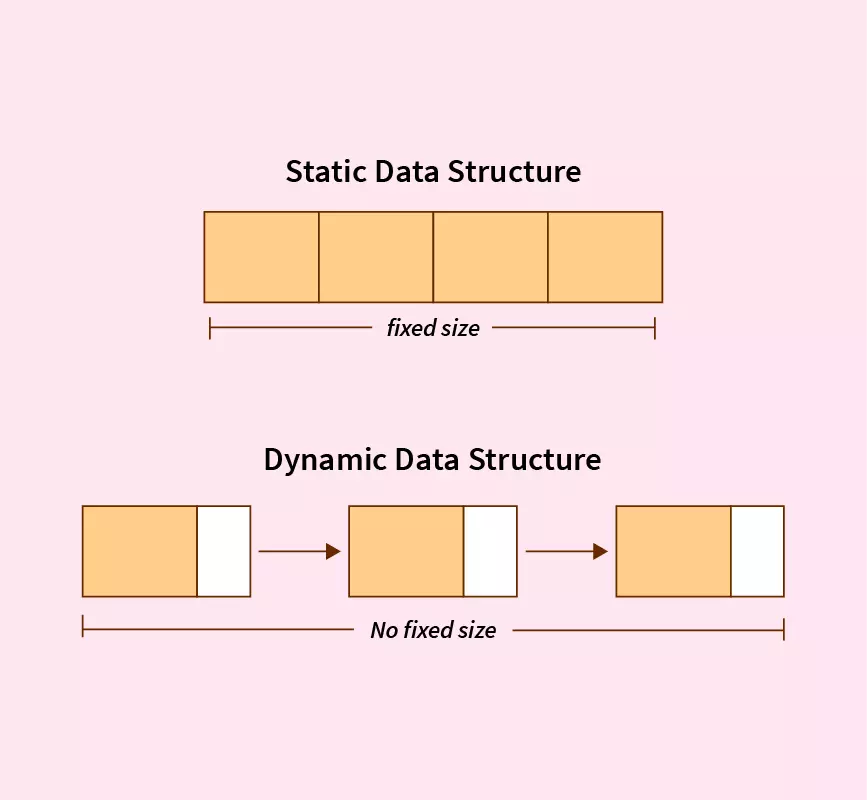
2. Static Data Structures
Definition
A static data structure has a fixed size, and memory is allocated at compile time. Once created, its size cannot be changed during program execution.
Examples
-
Array
-
Static stack
-
Static queue
Real-World Use Case
-
Fixed-size exam marks list
-
Predefined timetable slots
C++ Example (Static Array)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int marks[5] = {80, 85, 90, 75, 88};
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
cout << marks[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
Limitations
-
Wasted memory if not fully used
-
Size cannot grow or shrink
3. Dynamic Data Structures
Definition
A dynamic data structure can grow or shrink during runtime, and memory is allocated from the heap using dynamic memory allocation.
Examples
-
Linked List
-
Dynamic Array (Array List)
-
Tree
-
Graph
Real-World Use Case
-
Online shopping cart
-
Student registration system
-
Social media friend lists
C++ Example (Dynamic Array using new)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cout << "Enter size: ";
cin >> n;
int* arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = (i + 1) * 10;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
delete[] arr;
return 0;
}
4. Difference Between Static and Dynamic Data Structures
| Feature | Static Data Structure | Dynamic Data Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Allocation | Compile time | Runtime |
| Size | Fixed | Flexible |
| Memory Location | Stack | Heap |
| Efficiency | Faster | Slight overhead |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
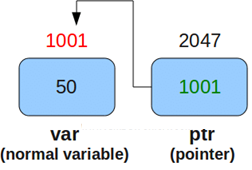
5. Pointers
Definition
A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable.
Why Pointers Are Important
-
Enable dynamic memory allocation
-
Essential for linked data structures
-
Improve performance by avoiding data copying
Real-World Analogy
A pointer is like a home address that tells you where someone lives instead of carrying the person with you.
C++ Example (Pointer Basics)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 10;
int* ptr = &x;
cout << "Value: " << x << endl;
cout << "Address: " << ptr << endl;
return 0;
}
6. Role of Pointers in Dynamic Data Structures
Pointers are the backbone of dynamic data structures. They connect nodes and manage memory efficiently.
Example: Linked List Node
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
int main() {
Node* head = new Node();
head->data = 10;
head->next = nullptr;
cout << head->data;
delete head;
return 0;
}
📌 Without pointers, linked lists, trees, and graphs cannot exist.
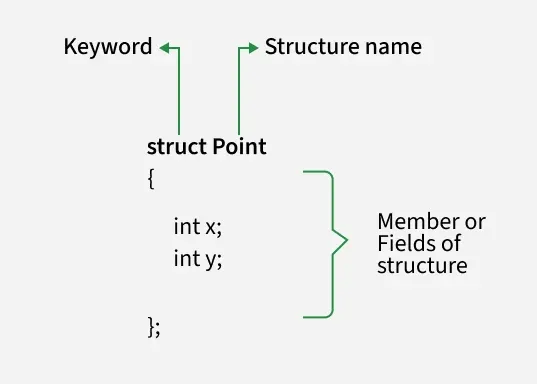
7. Structures in C++
Definition
A structure is a user-defined data type that groups variables of different data types under a single name.
Real-World Use Case
-
Student records
-
Employee information
-
Bank account details
C++ Example (Structure)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
int id;
string name;
float marks;
};
int main() {
Student s1 = {101, "Ali", 88.5};
cout << s1.name << " " << s1.marks;
return 0;
}
8. Structures with Pointers
Structures combined with pointers allow creation of dynamic and complex data structures.
Example: Structure Pointer
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student {
int id;
float marks;
};
int main() {
Student* s = new Student();
s->id = 102;
s->marks = 91.5;
cout << s->id << " " << s->marks;
delete s;
return 0;
}
9. Real-World Use Cases Summary
| Concept | Real-World Application |
|---|---|
| Static Data Structure | Fixed-size reports |
| Dynamic Data Structure | Online systems |
| Pointers | Memory management |
| Structures | Record management |
| Structures + Pointers | Databases, OS, networks |
9. Real-World Use Cases Summary
| Concept | Real-World Application |
|---|---|
| Static Data Structure | Fixed-size reports |
| Dynamic Data Structure | Online systems |
| Pointers | Memory management |
| Structures | Record management |
| Structures + Pointers | Databases, OS, networks |
FAQ Questions & Answers
1. What is a static data structure?
A static data structure has a fixed size, and memory is allocated at compile time. Its size cannot be changed during program execution.
2. What is a dynamic data structure?
A dynamic data structure can grow or shrink during runtime. Memory is allocated dynamically from the heap.
3. What is the main difference between static and dynamic data structures?
Static data structures have a fixed size, while dynamic data structures allow flexible resizing during program execution.
4. Why are dynamic data structures preferred in modern applications?
Dynamic data structures efficiently manage memory and adapt to changing data requirements, making them ideal for real-world applications.
5. What is a pointer in C++?
A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable, enabling efficient memory management and dynamic data handling.
6. Why are pointers important for dynamic data structures?
Pointers link data elements and allow dynamic memory allocation, which is essential for linked lists, trees, and graphs.
7. What is a structure in C++?
A structure is a user-defined data type that groups multiple variables of different data types under one name.
8. How are structures and pointers used together?
Structures combined with pointers help create dynamic and complex data structures such as linked lists and trees.
9. Which data structures use pointers extensively?
Linked lists, trees, graphs, and dynamic stacks and queues use pointers extensively.
10. When should static data structures be used?
Static data structures are suitable when the data size is known in advance and does not change frequently.