Content List
-
Introduction to Data Structures
-
Overview of Data Structures
-
Importance of Data Structures
-
Classification of Data Structures
-
Linear Data Structures
-
Non-Linear Data Structures
-
-
Operations on Data Structures
-
Abstract Data Types (ADT)
-
Conclusion
If you have not installed Visual Studio Code as a code editor, then visit the LINK.
1. Introduction to Data Structures
In computer science, data is the foundation of every program. How data is stored, organized, and accessed greatly affects the performance and efficiency of software.
This is where Data Structures play a vital role.
2. Overview of Data Structures
Definition
A Data Structure is a specialized way of organizing, storing, and managing data in memory so that it can be accessed and modified efficiently.
Real-Life Use Case
-
A contact list in a mobile phone uses arrays or linked lists.
-
A navigation app uses graphs to find the shortest path.
-
A web browser uses stacks to manage back and forward navigation.
Simple C++ Example (Array as a Data Structure)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int marks[5] = {85, 90, 78, 92, 88};
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << marks[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
3. Importance of Data Structures
Definition
The importance of data structures lies in their ability to optimize time and memory usage, making programs faster and more scalable.

Why Data Structures Are Important
-
Efficient data storage
-
Faster data access
-
Better memory utilization
-
Improved program performance
-
Essential for complex applications (AI, databases, OS)
Real Use Case
-
Search engines use trees and hash tables for fast searching.
-
Operating systems use queues for process scheduling.
4. Classification of Data Structures
Data Structures are mainly classified into Linear and Non-Linear data structures.
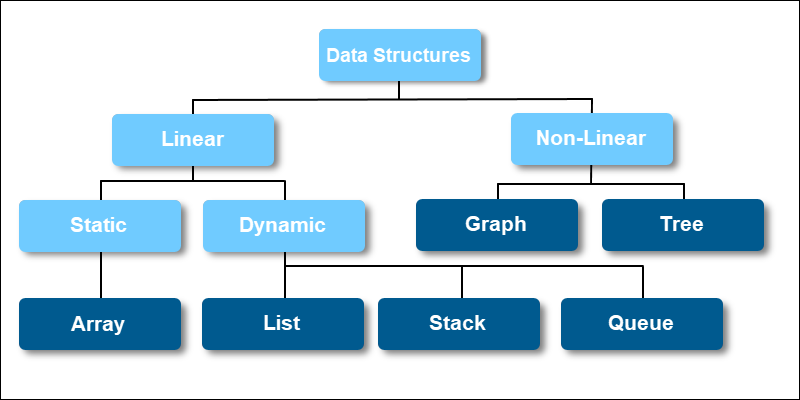
4.1 Linear Data Structures
Definition
Linear data structures store data in a sequential manner, where each element is connected to the next.
Examples
-
Array
-
Linked List
-
Stack
-
Queue
Real Use Case
-
Stack: Undo/Redo functionality in text editors
-
Queue: Ticket booking systems
C++ Example (Stack using Array)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int top = -1;
int stackArr[5];
void push(int value) {
if(top == 4)
cout << "Stack Overflow\n";
else
stackArr[++top] = value;
}
void display() {
for(int i = top; i >= 0; i--)
cout << stackArr[i] << " ";
}
int main() {
push(10);
push(20);
push(30);
display();
return 0;
}
4.2 Non-Linear Data Structures
Definition
Non-linear data structures store data in a hierarchical or graph-like structure, where elements are not arranged sequentially.
Examples
-
Tree
-
Graph
Real Use Case
-
Trees: File system hierarchy
-
Graphs: Social media networks
C++ Example (Binary Tree Node)
5. Operations on Data Structures
Definition
Operations on data structures are actions performed to manipulate stored data.
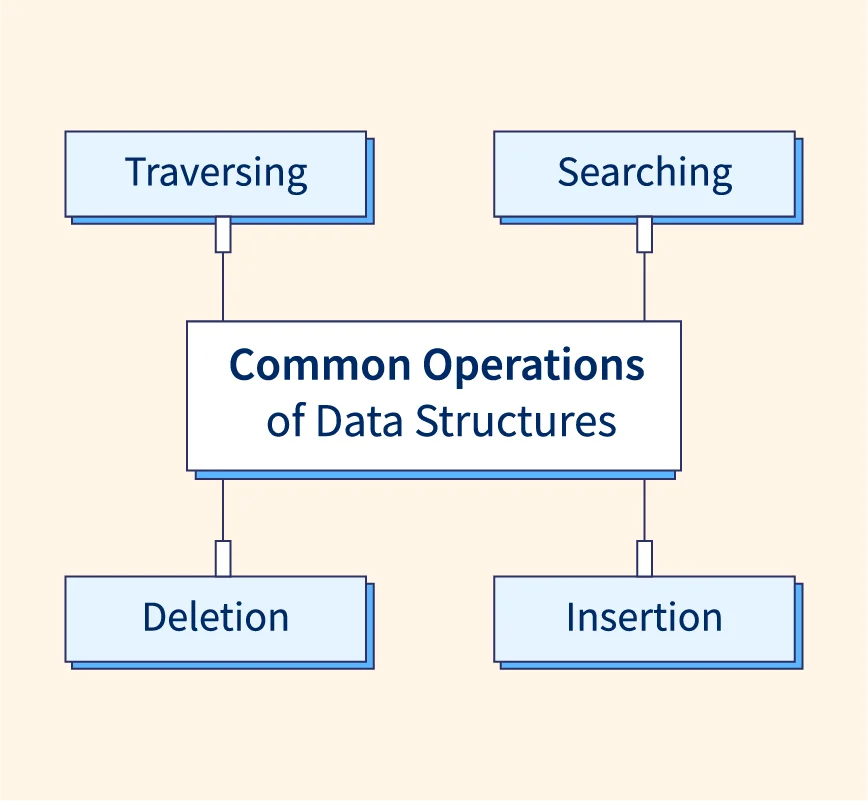
Common Operations
- Insertion
- Deletion
-
Traversal
-
Searching
-
Sorting
Real Use Case
-
Adding a new student record (Insertion)
-
Deleting old files (Deletion)
-
Searching a contact name (Searching)
C++ Example (Insertion & Traversal in Array)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40};
int n = 4;
arr[n] = 50;
n++;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
6. Abstract Data Types (ADT)
Definition
An Abstract Data Type (ADT) is a logical description of a data structure that defines what operations can be performed, without specifying how they are implemented.
Key Idea
-
Focuses on behavior, not implementation
-
Implementation can vary
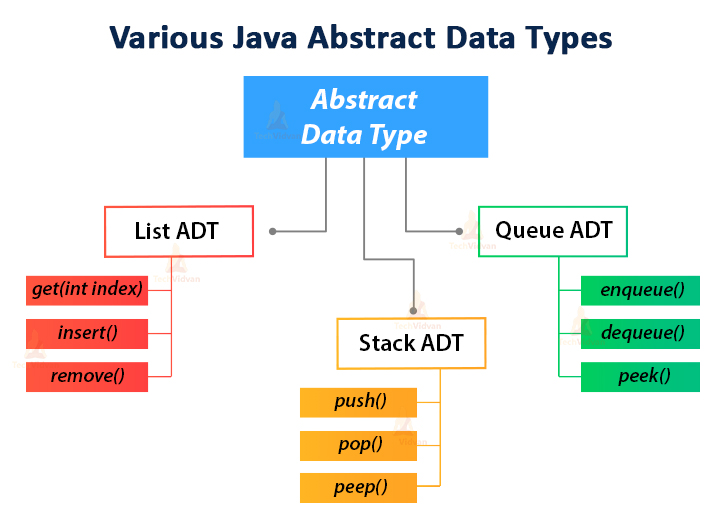
Examples of ADT
-
Stack ADT
-
Queue ADT
-
List ADT
Real Use Case
-
A Stack ADT defines operations like push and pop, regardless of whether it is implemented using arrays or linked lists.
C++ Example (Stack ADT Concept)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Stack {
int top;
int arr[5];
public:
Stack() {
top = -1;
}
void push(int x) {
if(top == 4)
cout << "Overflow\n";
else
arr[++top] = x;
}
void pop() {
if(top == -1)
cout << "Underflow\n";
else
top--;
}
void display() {
for(int i = top; i >= 0; i--)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
};
int main() {
Stack s;
s.push(5);
s.push(15);
s.push(25);
s.display();
return 0;
}
7. Conclusion
Data Structures are the backbone of efficient programming. Understanding their types, operations, and abstract behavior enables developers to design optimized and scalable solutions.
Mastery of data structures is essential for software development, competitive programming, and system design.
1. What is a data structure?
A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data in memory so that it can be accessed, modified, and processed efficiently.
2. Why are data structures important in programming?
Data structures improve program efficiency by optimizing memory usage, reducing execution time, and enabling scalable software design.
3. What are the main types of data structures?
Data structures are mainly classified into:
-
Linear data structures (Array, Stack, Queue, Linked List)
-
Non-linear data structures (Tree, Graph)
4. What is the difference between linear and non-linear data structures?
Linear data structures store elements sequentially, while non-linear data structures store data in hierarchical or network form.
5. What operations are performed on data structures?
Common operations include insertion, deletion, traversal, searching, and sorting.
6. What is an Abstract Data Type (ADT)?
An Abstract Data Type defines a data structure logically by specifying operations without revealing implementation details.
7. What is the difference between ADT and data structure?
ADT focuses on what operations are performed, while a data structure focuses on how data is stored in memory.
8. Which data structure is best for undo and redo operations?
A stack data structure is best suited because it follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle.
9. Which data structure is used in real-world applications like navigation systems?
Graphs are used in navigation systems to represent locations and routes efficiently.
10. Why is C++ commonly used to learn data structures?
C++ provides low-level memory control, pointers, and high performance, making it ideal for understanding data structures deeply.
Explore easy-to-understand tutorials, practical C++ examples, and real-world applications of data structures and core programming concepts.
Join our blog to receive regular updates and sharpen your problem-solving skills with confidence.





