Content List
-
Introduction to Array List
-
What is an Array List?
-
Importance of Array List
-
Characteristics of Array List
-
Array List vs Array
-
Operations on Array List
-
Insertion
-
Deletion
-
Traversal
-
Searching
-
Updating
-
-
Real-World Use Cases of Array List
-
Implementation of Array List in C++
-
Advantages and Limitations
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to Array List
In modern software applications, data is rarely static. Programs often need to add, remove, or update elements dynamically. Traditional arrays have a fixed size, which makes them less flexible.
To overcome this limitation, the concept of an Array List is widely used.
2. What is an Array List?
Definition
An Array List is a dynamic data structure that stores elements in a contiguous memory location like an array but can grow or shrink in size automatically during runtime.
Unlike a simple array, an array list does not require the size to be defined in advance.
3. Importance of Array List
Why Array List is Important
-
Dynamic resizing
-
Efficient random access
-
Easy insertion and deletion
-
Widely used in real-world applications
Real-Life Example
-
A shopping cart where items can be added or removed
-
A playlist where songs change dynamically
-
A student list that grows each semester
4. Characteristics of Array List
-
Stores elements in contiguous memory
-
Supports index-based access
-
Automatically resizes when capacity is exceeded
-
Maintains insertion order
-
Allows duplicate elements
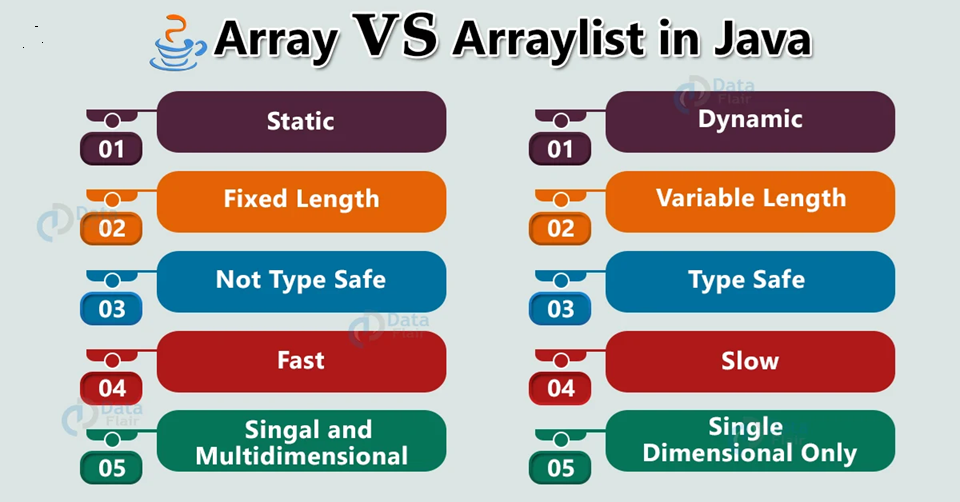
5. ArrayList vs. Array
| Feature | Array | Array List |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Fixed | Dynamic |
| Memory | Static | Dynamic |
| Insertion | Difficult | Easy |
| Deletion | Difficult | Easy |
| Access | Fast | Fast |
6. Operations on ArrayList
6.1 Insertion Operation
Definition
Insertion adds a new element to the array list. If the list is full, it automatically increases its size.
Use Case
Adding a new product to an online store catalog.
C++ Example (Insertion)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[10] = {10, 20, 30};
int size = 3;
arr[size] = 40;
size++;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
6.2 Deletion Operation
Definition
Deletion removes an element from a specified index and shifts remaining elements.
Use Case
Removing an item from a shopping cart.
C++ Example (Deletion)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[10] = {10, 20, 30, 40};
int size = 4;
int pos = 1;
for(int i = pos; i < size - 1; i++)
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
size--;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
6.3 Traversal Operation
Definition
Traversal means accessing each element of the array list one by one.
Use Case
Displaying all students in a class list.
C++ Example (Traversal)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = {5, 15, 25, 35};
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
6.4 Searching Operation
Definition
Searching finds whether an element exists in the array list.
Use Case
Searching a contact name in a phonebook.
C++ Example (Searching)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40};
int key = 30;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if(arr[i] == key) {
cout << "Element found at index " << i;
return 0;
}
}
cout << "Element not found";
return 0;
}
6.5 Updating Operation
Definition
Updating modifies an existing element in the array list.
Use Case
Updating a product price in inventory.
C++ Example (Updating)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30};
arr[1] = 25;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
. Real-World Use Cases of Array List
-
Dynamic menus in applications
-
Online booking systems
-
Student record management
-
Game score tracking
-
E-commerce platforms
8. Implementation of Array List in C++ (Using Class)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class ArrayList {
int arr[10];
int size;
public:
ArrayList() {
size = 0;
}
void add(int value) {
arr[size++] = value;
}
void display() {
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
};
int main() {
ArrayList list;
list.add(10);
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.display();
return 0;
}
9. Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
-
Dynamic size
-
Fast access using index
-
Easy to implement
Limitations
-
Shifting elements is costly
-
Fixed capacity in basic implementation
-
Memory reallocation overhead
10. Conclusion
An Array List is one of the most useful dynamic data structures in programming. It combines the speed of arrays with the flexibility of dynamic memory allocation. Understanding its operations—insertion, deletion, traversal, searching, and updating—is essential for building efficient and scalable software applications.
Mastering array lists builds a strong foundation for advanced data structures and algorithms.
Are you interested in developing mobile application development skills? You may visit the link below:
https://onlineskilllab.com/category/flutter-development/
If you are learning and enjoying, subscribe to our blog for daily updates.







