Introduction
Mobile applications have become a core part of modern digital life. From online banking and e-commerce to education, healthcare, and entertainment, mobile apps power everyday activities. As businesses increasingly rely on mobile-first strategies, the demand for skilled mobile application developers continues to grow globally.
This course-oriented blog explains the fundamental concepts of mobile applications, followed by a clear comparison of Native and Cross-Platform apps, and then provides step-by-step practical implementation using Flutter and Dart, one of the most in-demand cross-platform technologies today.

Visit the last lesson. 01: How to Install Flutter Using Android Studio on Windows
1. Introduction to Mobile Applications
Topic Content Overview
In this section, learners are introduced to:
-
What mobile applications are
-
Types of mobile applications
-
How mobile apps work
-
Mobile app development lifecycle
-
Popular technologies used in mobile app development
This foundation helps students understand why mobile development matters and how apps are designed, built, tested, and deployed.
Definition of Mobile Application
A mobile application is a software program specifically designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. These applications interact with device hardware (camera, GPS, sensors), operating systems (Android, iOS), and cloud services to deliver functionality to users.
Types of Mobile Applications
-
Native Applications: Built for a specific platform (Android or iOS)
-
Web Applications: Run inside a mobile browser
-
Hybrid Applications: Web apps wrapped in a native container
-
Cross-Platform Applications: Single codebase for multiple platforms
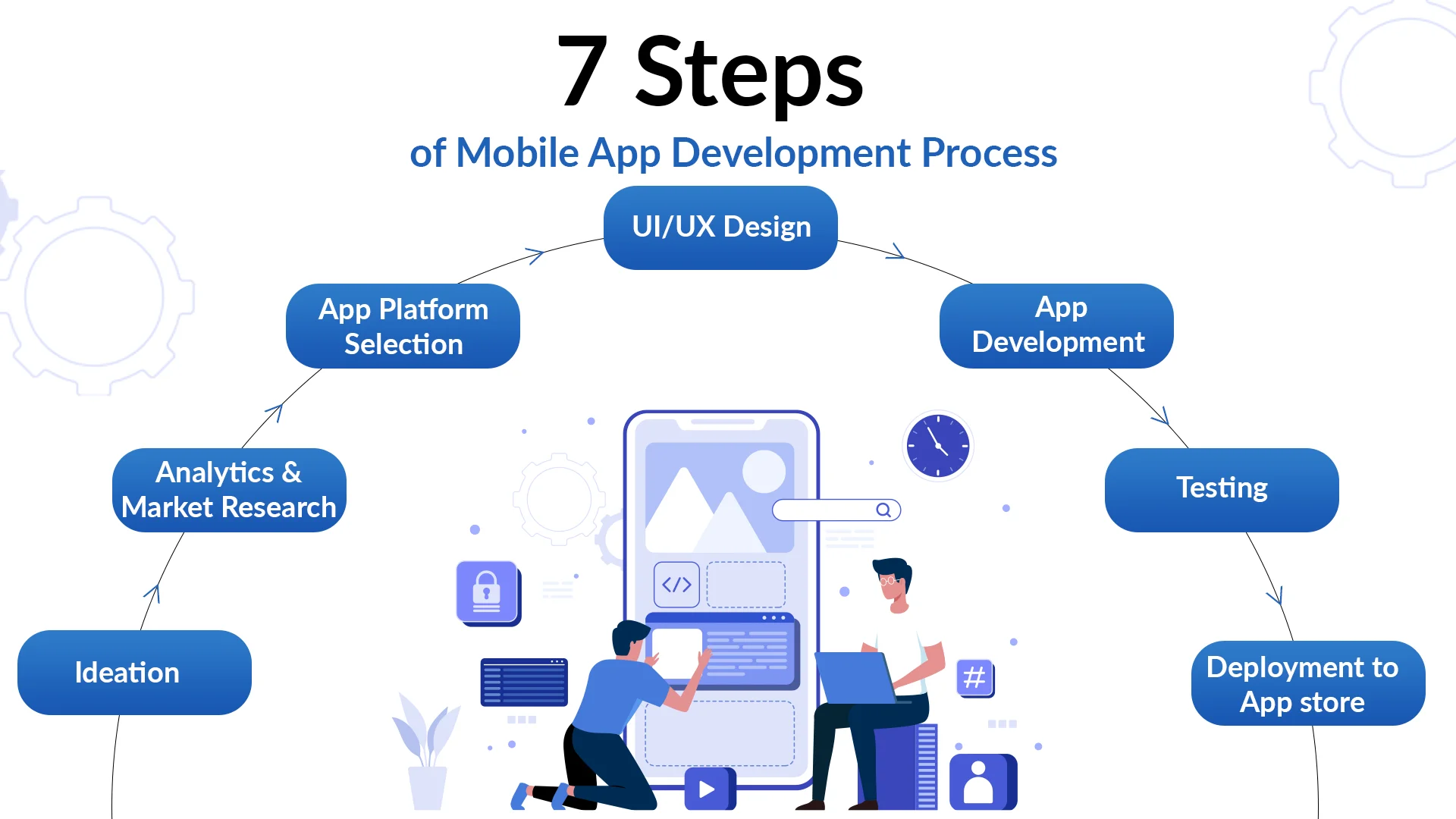
Mobile Application Development Lifecycle
-
Requirement Analysis
-
UI/UX Design
-
Development
-
Testing
-
Deployment
-
Maintenance & Updates
Step-by-Step Implementation (Flutter Example)
Step 1: Install Flutter SDK
-
Download Flutter from the official Flutter website
-
Set environment variables
-
Verify installation using the command on CMD: flutter doctor
Step 2: Create Your First Flutter Project
flutter create mobile_intro_app
cd mobile_intro_app
flutter run
Step 3: Basic Flutter App Structure (Dart)
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Mobile App Intro")),
body: Center(
child: Text(
"Welcome to Mobile Application Development",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
),
),
);
}
}
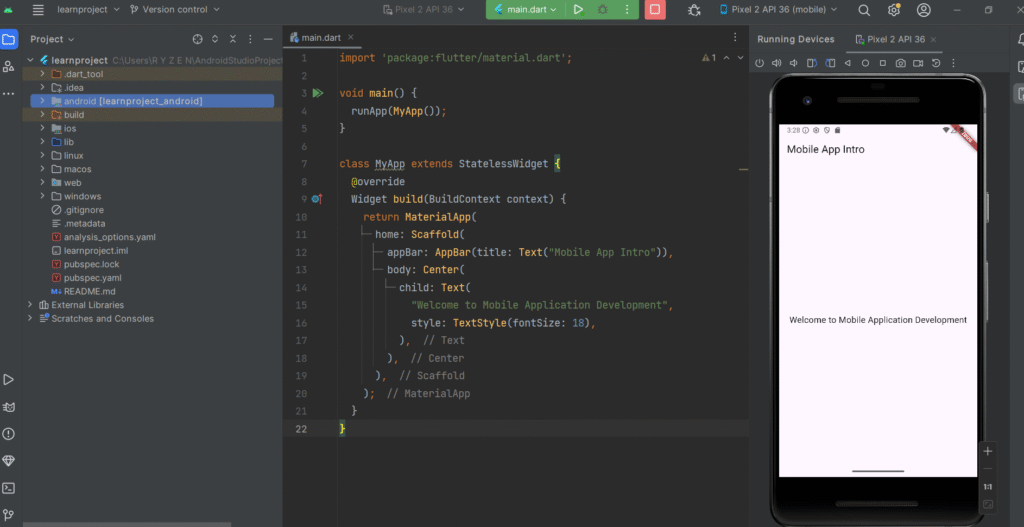
Real-Time Use Case:
This example represents a welcome screen of a mobile learning application used in universities or training institutes.
2. Native & Cross-Platform Applications
Topic Content Overview
This section explains:
-
What native apps are
-
What cross-platform apps are
-
Differences between native and cross-platform development
-
When to choose each approach
-
Real-world examples
-
Flutter as a cross-platform solution
Definition
Native Applications
Native applications are developed specifically for a single platform using platform-specific languages:
-
Android: Java / Kotlin
-
iOS: Swift / Objective-C
Cross-Platform Applications
Cross-platform applications are developed using a single codebase that runs on multiple platforms such as Android and iOS.
Native vs Cross-Platform Comparison
| Feature | Native Apps | Cross-Platform Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Codebase | Separate | Single |
| Performance | Very High | High |
| Development Cost | High | Lower |
| Time to Market | Longer | Faster |
| Examples | WhatsApp, Google Maps | Alibaba, BMW App |
Why Flutter for Cross-Platform Development?
-
Uses Dart language
-
Single codebase for Android & iOS
-
High performance using Skia engine
-
Rich UI with customizable widgets
-
Backed by Google
Step-by-Step Flutter Implementation (Cross-Platform)
Step 1: Create Cross-Platform App
flutter create cross_platform_app
Step 2: UI Code (Single Codebase)
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(CrossPlatformApp());
}
class CrossPlatformApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Cross Platform App")),
body: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Icon(Icons.phone_android, size: 60),
SizedBox(height: 20),
Text(
"Runs on Android & iOS",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20),
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
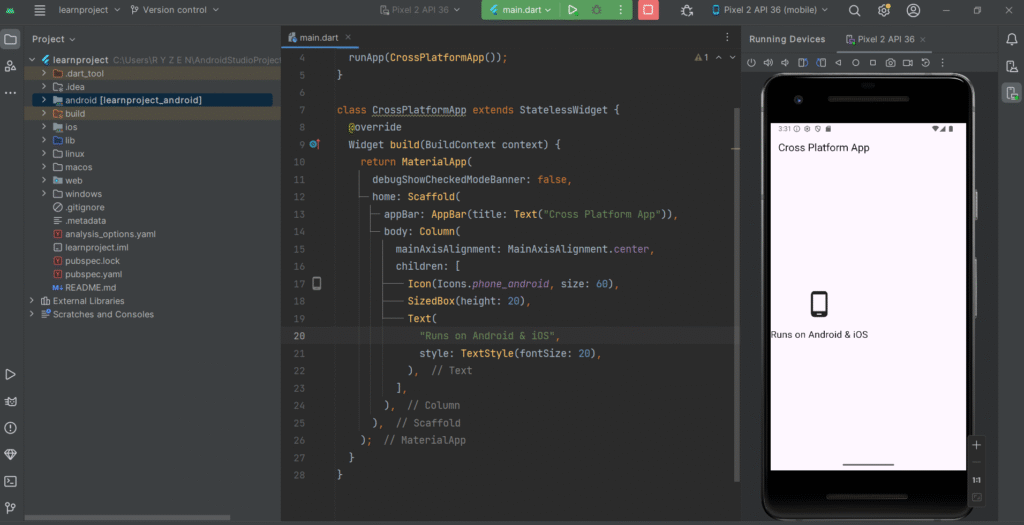
Real-Time Example:
This single Flutter codebase can be deployed:
-
As an Android app (.apk)
-
As an iOS app (.ipa)
Used in e-commerce apps, learning management systems, and startup MVPs.
Step 3: Run on Multiple Platforms
flutter run -d android
flutter run -d ios
Conclusion
Mobile application development is a high-demand skill, and understanding the difference between Native and Cross-Platform development is essential for modern developers. Flutter provides an efficient, scalable, and industry-ready solution for building real-world mobile applications using a single codebase.
This step-by-step Flutter approach ensures learners gain both theoretical understanding and practical experience, making it ideal for academic courses, bootcamps, and professional training programs.
Are you ready for tech interviews? Check your OOP concepts by visiting the link.
Stay updated with the latest lessons in mobile application development, Flutter tutorials, and real-world app development examples. Subscribe now to receive expert insights, step-by-step guides, and course updates directly in your inbox. Never miss an opportunity to enhance your mobile development skills and stay ahead in the tech industry.