Doubly Linked List Operations (With C++ Examples)
A Doubly Linked List (DLL) is an advanced linear data structure where each node contains three parts:
-
Data
-
Pointer to the previous node
-
Pointer to the next node
This two-way linking allows forward and backward traversal, making certain operations more efficient than in singly linked lists.
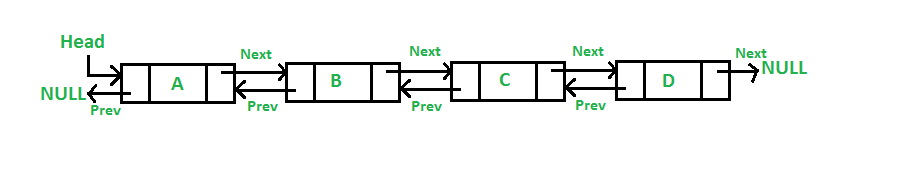
Structure of a Doubly Linked List Node
struct Node {
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
};
You may visit Lesson 06: More Operations of Singly Linked List (With C++ Examples)
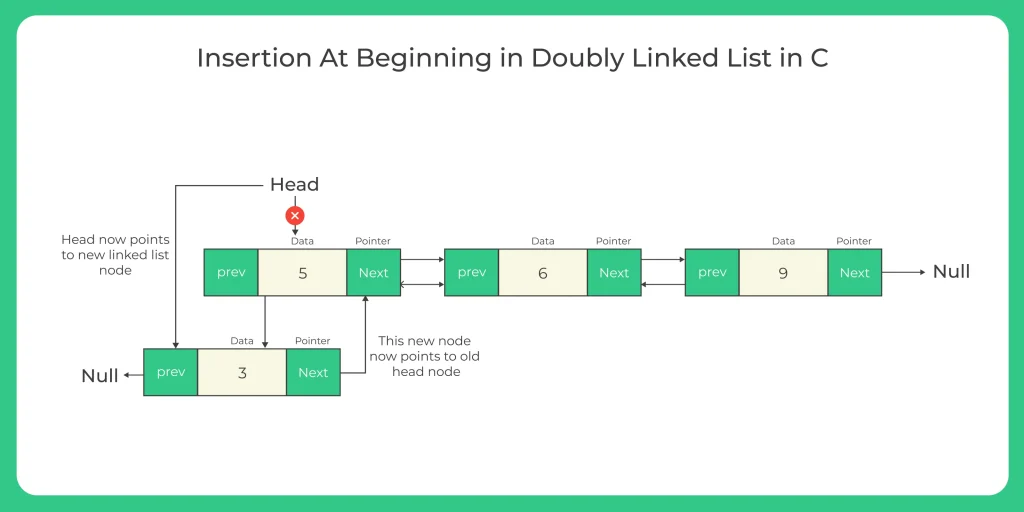
1️⃣ Insert at the Beginning
📌 Definition
Inserts a new node at the start (head) of the doubly linked list.
💡 Real-World Use Case
Adding a recently opened file to the beginning of a history list.
💻 C++ Code
void insertAtStart(Node*& head, int value) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = value;
newNode->prev = nullptr;
newNode->next = head;
if (head != nullptr)
head->prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
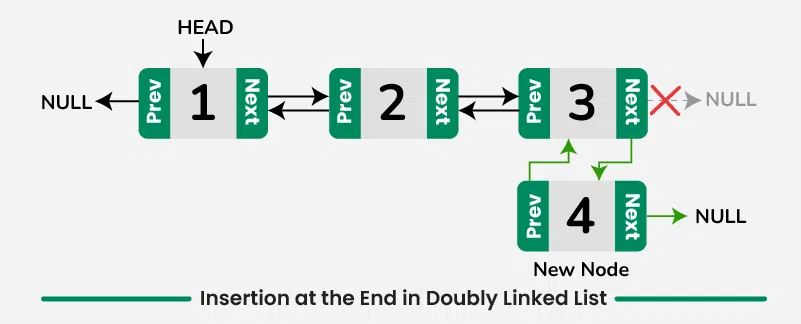
2️⃣ Insert at the End
📌 Definition
Adds a new node at the end (tail) of the list.
💡 Real-World Use Case
Appending songs to the end of a music playlist.
💻 C++ Code
void insertAtEnd(Node*& head, int value) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = nullptr;
if (head == nullptr) {
newNode->prev = nullptr;
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
while (temp->next != nullptr)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = temp;
}
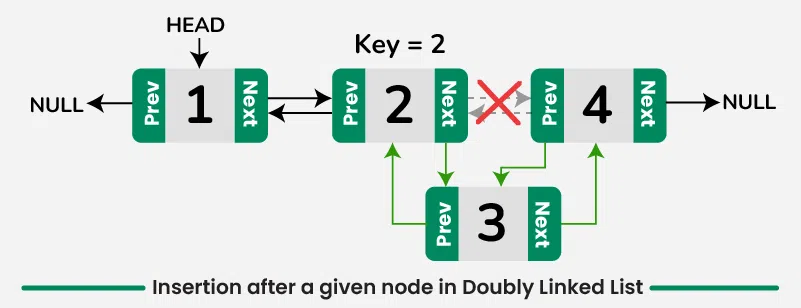
3️⃣ Insert After a Specific Value
📌 Definition
Inserts a new node after a given value.
💡 Real-World Use Case
Inserting a new step after an existing step in a workflow.
💻 C++ Code
void insertAfterValue(Node* head, int target, int value) {
Node* temp = head;
while (temp != nullptr && temp->data != target)
temp = temp->next;
if (temp != nullptr) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = temp->next;
newNode->prev = temp;
if (temp->next != nullptr)
temp->next->prev = newNode;
temp->next = newNode;
}
}
4️⃣ Delete from the Beginning
📌 Definition
Deletes the first node of the doubly linked list.
💡 Real-World Use Case
Removing the oldest entry from a cache.
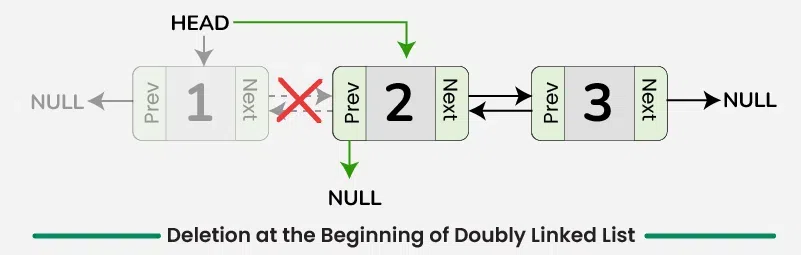
💻 C++ Code
void deleteFromStart(Node*& head) {
if (head == nullptr) return;
Node* temp = head;
head = head->next;
if (head != nullptr)
head->prev = nullptr;
delete temp;
}
5️⃣ Delete from the End
📌 Definition
Deletes the last node of the list.
💡 Real-World Use Case
Removing the last undo operation.

💻 C++ Code
void deleteFromEnd(Node*& head) {
if (head == nullptr) return;
if (head->next == nullptr) {
delete head;
head = nullptr;
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
while (temp->next != nullptr)
temp = temp->next;
temp->prev->next = nullptr;
delete temp;
}
📊 Time Complexity Summary
| Operation | Time Complexity |
|---|---|
| Insert at Start | O(1) |
| Insert at End | O(n) |
| Insert After Value | O(n) |
| Delete from Start | O(1) |
| Delete from End | O(n) |
| Traversal | O(n) |
✅ Advantages of Doubly Linked List
-
Bidirectional traversal
-
Easier deletion operations
-
Efficient backward navigation
❌ Disadvantages
-
Extra memory overhead
-
More complex pointer handling
🎯 Key Takeaway
A doubly linked list is ideal when two-way traversal and efficient deletion are required, such as in navigation systems, editors, and operating systems.
Are you interested in developing mobile application development skills? You may visit the link below:
https://onlineskilllab.com/2025/11/18/how-to-build-a-complete-flutter-authentication-system-with-firebase-login-signup-reset-password-dashboard/
If you are learning and enjoying, subscribe to our blog for daily updates.





