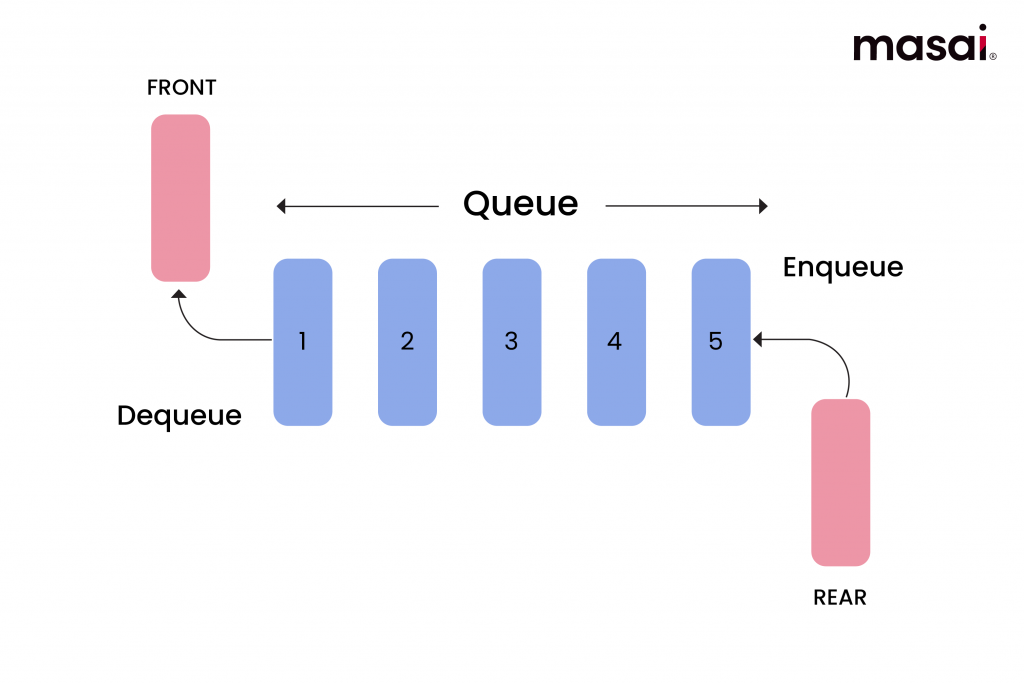
Introduction to Queue in C++
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle.
This means the first element inserted is the first element removed.
Queues are widely used in task scheduling, resource management, and data buffering.
Visit the last lesson: Infix to Postfix Conversion Using Stack
Definition of Queue
A queue is a collection of elements supporting the following main operations:
-
Enqueue – Add an element to the rear of the queue
-
Dequeue – Remove an element from the front of the queue
Additional operations:
-
Front/Peek – Access the front element without removing it
-
isEmpty – Check if the queue is empty
-
isFull – Check if the queue is full (only for static queues)
🔹 Real-World Use Cases
-
CPU Scheduling: Round-robin scheduling uses queues to manage processes
-
Print Queues: Documents are printed in the order they arrive
-
Network Buffers: Packets are transmitted in FIFO order
-
Customer Service Systems: First customer served first
1️⃣ Static Implementation of Queue
Static queues are implemented using arrays with a fixed size.

💻 C++ Code (Static Queue)
#include <iostream>
#define MAX 5
using namespace std;
class Queue {
int arr[MAX];
int front, rear;
public:
Queue() { front = -1; rear = -1; }
bool isEmpty() { return front == -1; }
bool isFull() { return rear == MAX - 1; }
void enqueue(int x) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Queue Overflow\n";
return;
}
if (isEmpty()) front = 0;
arr[++rear] = x;
cout << x << " enqueued to queue\n";
}
void dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue Underflow\n";
return;
}
cout << arr[front] << " dequeued from queue\n";
if (front == rear) front = rear = -1;
else front++;
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
return arr[front];
}
};
int main() {
Queue q;
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.enqueue(30);
cout << "Front element: " << q.peek() << endl;
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
return 0;
}
2️⃣ Dynamic Implementation of Queue
Dynamic queues are implemented using linked lists, allowing flexible memory usage.
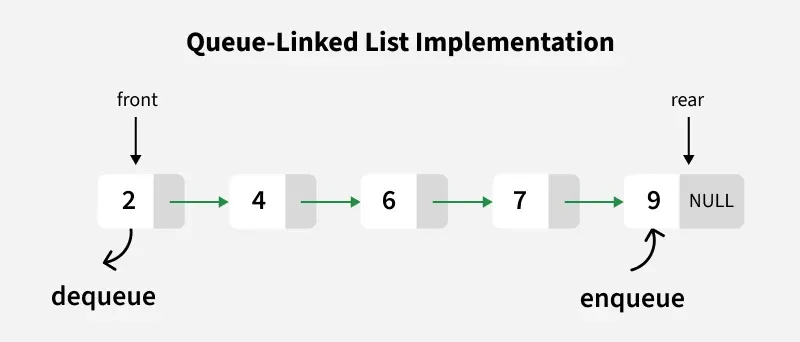
💻 C++ Code (Dynamic Queue)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
class Queue {
Node *front, *rear;
public:
Queue() { front = rear = nullptr; }
bool isEmpty() { return front == nullptr; }
void enqueue(int value) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = nullptr;
if (rear == nullptr) {
front = rear = newNode;
} else {
rear->next = newNode;
rear = newNode;
}
cout << value << " enqueued to queue\n";
}
void dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue Underflow\n";
return;
}
Node* temp = front;
front = front->next;
if (front == nullptr) rear = nullptr;
cout << temp->data << " dequeued from queue\n";
delete temp;
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
return front->data;
}
};
int main() {
Queue q;
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.enqueue(30);
cout << "Front element: " << q.peek() << endl;
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
return 0;
}
🔹 Operations Summary
| Operation | Description | Static Queue | Dynamic Queue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enqueue | Insert element | O(1) | O(1) |
| Dequeue | Remove element | O(1) | O(1) |
| Peek | Access front | O(1) | O(1) |
| isEmpty | Check if empty | O(1) | O(1) |
| isFull | Check if full | O(1) | Not required |
Key Takeaways
-
Queues follow FIFO principle.
-
Static queues are simple but memory-limited.
-
Dynamic queues use linked lists and are memory-efficient.
-
Queues are widely used in real-world applications such as scheduling, buffers, and task management.
Interview Questions & Answers for Queue
-
What is a queue?
A queue is a FIFO (First In, First Out) data structure where the first element added is the first element removed. -
What are the main operations of a queue?
-
Enqueue: Add element to the rear
-
Dequeue: Remove element from the front
-
Peek/Front: Access front element
-
isEmpty: Check if queue is empty
-
isFull: Check if queue is full (static queue only)
-
What is the difference between a stack and a queue?
-
Stack: LIFO (Last In, First Out)
-
Queue: FIFO (First In, First Out)
-
How is a queue implemented in C++?
-
Static queue: Using arrays with a fixed size
-
Dynamic queue: Using linked lists for flexible memory
-
What is the time complexity of enqueue and dequeue operations?
O(1) for both static and dynamic queue. -
What happens if you try to enqueue in a full static queue?
It causes Queue Overflow. -
What happens if you dequeue from an empty queue?
It causes Queue Underflow.
-
What is a circular queue?
A circular queue connects the rear back to the front, making it memory-efficient and preventing wasted space in static arrays. -
Why is a dynamic queue more memory-efficient than a static queue?
Because it grows and shrinks dynamically as elements are added or removed, avoiding unused memory. -
What are some real-world applications of queues?
-
CPU scheduling (round-robin)
-
Print spooling
-
Network packet buffering
-
Customer service ticketing
11. Which queue implementation is better for unknown data size?
Dynamic queue using linked lists.
12. Why are queues used in CPU scheduling?
Because processes are executed in the order they arrive (FIFO principle).
13. What could go wrong if you forget to check if the queue is empty before dequeueing?
It will cause runtime errors or crash the program.
Are you interested in developing mobile application development skills? You may visit the link below:
If you are learning and enjoying, subscribe to our blog for daily updates